Recently, Professor Xiong's team from the Institute of Aging Research of GDMU, published the latest research results "circGNAQ, a circular RNA enriched in vascular endothelium, inhibits endothelial cell senescence and atherosclerosis progression" in the internationally renowned academic journal Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids (IF 8.886). This study revealed for the first time that circGNAQ inhibits endothelial cell senescence and atherosclerosis progression through circGNAQ/miR-146a-5p/PLK2 pathway.

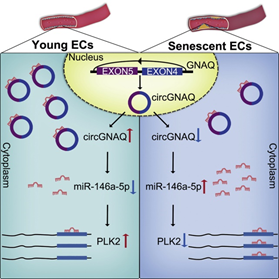
Aging is an important risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, and the incidence of cardiovascular events increases with age. Recent studies have shown that the integrity of EC function is compromised with aging, and EC senescence plays a pivotal role in the evolution of age-related vascular disorders, such as atherosclerosis. Therefore, it is critical to explore the mechanisms underlying EC senescence to better predict and prevent endothelial contributions to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases associated with aging. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are endogenous RNA molecules with covalently closed-loop structures, which have been reported to be abnormally expressed in many human diseases. In this study, Xiong's team found a novel circRNA circGNAQ can be decreased in senescent ECs and aging blood vessels. Interestingly, circGNAQ was enriched in vascular endothelium, suggesting that circGNAQ could be involved in regulating vascular function. Moreover, circGNAQ delayed cellular senescence by harboring miR-146a-5p to abolish the suppressive effect on the target gene PLK2 in ECs. Additionally, circGNAQ overexpression inhibited EC senescence and prevented atherosclerosis progression in Ldlr-/- mice. Hence, circGNAQ-based gene therapy could serve as a novel therapeutic strategy to protect against atherosclerosis development.
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, the program for Training High-level Talents of Dongguan, and the discipline construction project of Guangdong Medical University. Graduate students Wu Weipeng , Zhou Mengyuan , Liu Dongliang , and Min Xue are the co-first authors of the paper, and the corresponding author is Professor Xing-dong Xiong.

Paper link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34552819/
Writer: Zhou Tong
Translator:Xiong Xingdong
Editor: Tang Zhipeng